What is DMAIC?
DMAIC is a business improvement and problem-solving method used to improve business performance. During the DMAIC process, improvement happens project by project; a “project” can be best defined as a “problem scheduled for a solution.” This means management has decided it is important enough to schedule the resources it needs to get the problem solved.
There are many projects carried out in organizations, such as:
- Improving employee and customer satisfaction
- Decreasing the time from order to shipment received
- Launching new services
A great improvement project is a problem that must be resolved. It may be to reduce waste, improve customer satisfaction, or improve reduce defects. This is usually a process, customer, or product issue.
DMAIC Methodology and Phases
Successful projects follow the Lean Six Sigma DMAIC methodology, which encompasses five distinct stages:
- Define
- Measure
- Analyze
- Improve
- Control
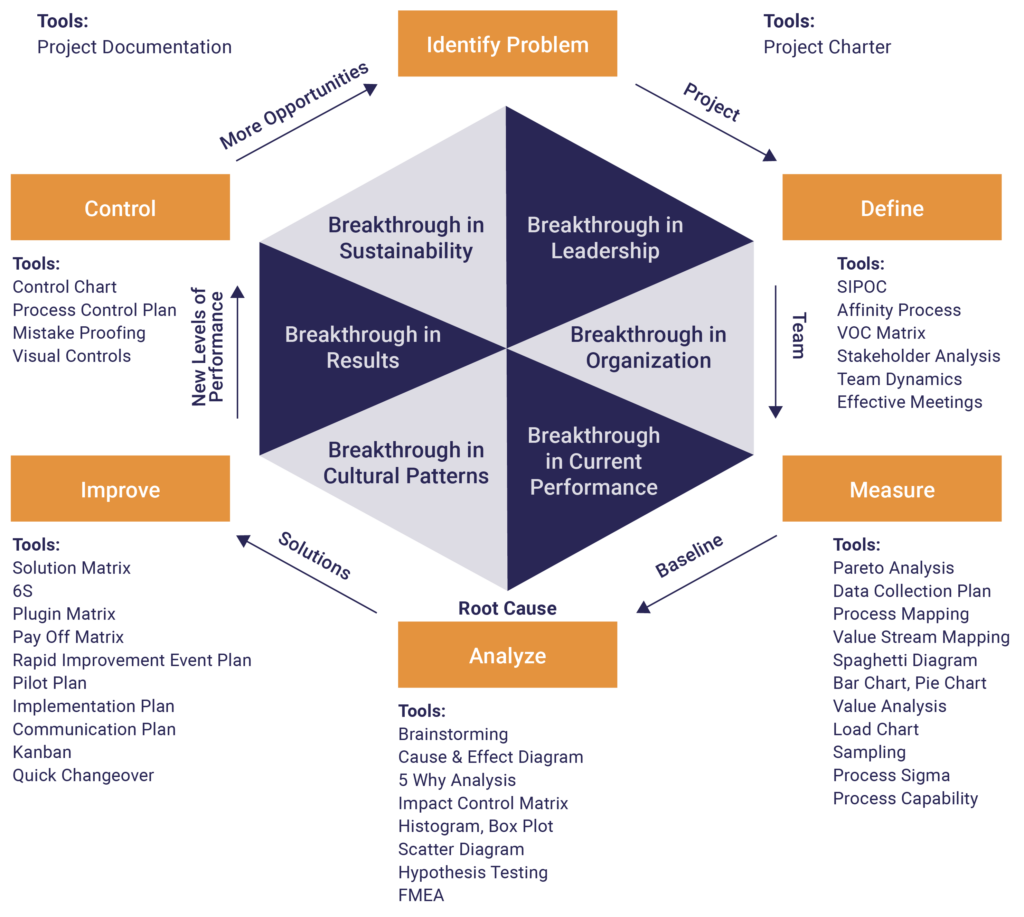
DMAIC methodology is typically used as a part of a larger Lean Six Sigma program to create ‘breakthroughs’ in an organization. Each project is assigned to a Lean or Six Sigma leader called a Black or Green Belt and a team of subject matter experts.
Once a problem is identified by an organization’s senior management, a project team is selected to resolve it. This team simply follows their project charter through the five steps of the DMAIC methodology, by applying appropriate DMAIC tools during each DMAIC step.
Define
In the first phase of the DMAIC process, the project team better defines the problem they have been given by leadership, asking questions to both internal and external customers to affirm that the issue really exists.
Tools Used in the Define Phase
- Stakeholder analysis
- Collection of the voice of the customer using the voice of the customer matrix
- Voice of the customer to critical to quality translation
- High-level process map (SIPOC diagram)
Measure
During the measure phase, the project team begins assessing the current baseline performance of the problem, collecting and interpreting the available data on current performance. This often leads to a redefining of the problem to focus on the most pressing or ‘vital few issues.’
Tools Used in the Measure Phase
- Juran’s Pareto Analysis
- Data Collection Plan
- Detailed Process Mapping
- 6S
- Value Stream Maps
Analyze
Analyze is the third phase of the DMAIC methodology. During this phase, the project team collects and uses data to prove theories of root cause or causes of the problem. These root causes are known as ‘Project Xs’. By the conclusion of this phase, the team will have narrowed down their multiple theories to a vital potential few root causes to test and prove true or false.
Tools Used in the Analyze Phase
- Calculating Sigma Level
- Graphs and Charts
- Brainstorming
- Stratification
- Histograms
- Box Plots
- Scatter Diagrams
- Cause and Effect Diagrams
- 5 Why Analysis
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
- Impact Control Matrix
Improve
This is when the project team begins the remedial journey and begins acting on what they have learned by making improvements. At this point, the team will:
- Generate alternative solutions
- Design the solution (including designs for culture, and designs for control)
- Prove the effectiveness of the solution
- Implement the solution
Tools Used in the Improve Phase
- Brainstorming
- Solution Matrix
- Barriers and Aids Chart
- Pilot Study
- Mistake Proofing
- Benchmarking
- Pugh Matrix
Control
The fifth and final phase of the DMAIC methodology, this is when the project team ensures that gains made during the improve phase are held, and the problem does not recur. To ensure this, the team needs to:
- Identify control subjects
- Establish a measurement for control
- Establish standards of performance
- Measure actual performance
- Compare actual measured performance to standards
- Take action on the difference
Tools Used in the Control Phase
- Process Control Plan
- Control Charts
- Error proofing/poke yoke
- Change management
Impact of Lean Six Sigma DMAIC Methodology
The Lean Six Sigma DMAIC methodology provide a framework to assist organizations in attaining superior quality, sustainable results, and financial returns. They do this by:
- Assuring that quality thinking becomes the way of doing business, creating a focus on customers and building customer loyalty.
- Applying proven quality tools to improve goods and services, and achieve breakthrough performance.
- Defining quality process performance metrics that tie to organizational goals.
- Creating a quality culture that is fun and provides a pragmatic way to achieve greater levels of process quality.
- Identifying projects to drive the improvement that will yield superior quality and sustainable results.
The DMAIC methodology is a guide to keep the team and project moving forward in an efficient way. We often refer to the DMAIC steps as the “boss of the project.” Although there is a team leader, the steps are the boss because one must follow the steps to complete the project. Skipping a step could cause an organization to waste money, cause unnecessary culture issues and solutions that do not hold gains.
For more information on DMAIC and how Juran can help you leverage it to improve business quality and productivity, please get in touch with the team.
| Check out Juran’s LSS Training Courses |
| Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt |
| Lean Six Sigma Green Belt |
| Lean Six Sigma Black Belt |
| Upgrade to Black Belt |
| Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt |
| Lean Expert Program |






